
Chick embryo development provides a remarkable model for studying vertebrate embryogenesis‚ offering accessible visualization of development stages.
Detailed diagrams and charts‚ often available as PDFs‚ illustrate the 21-day journey from fertilization to hatching‚ showcasing key morphological changes.
Understanding this process is fundamental to comprehending the origins of life and the intricacies of organ system formation‚ as highlighted in embryology studies.
Overview of Embryogenesis
Embryogenesis‚ the process of cell division and differentiation leading to embryo formation‚ is exceptionally well-documented in the chick embryo. This development‚ spanning 21 days‚ provides a clear visual timeline‚ often detailed in comprehensive chick embryo development stages PDF guides.
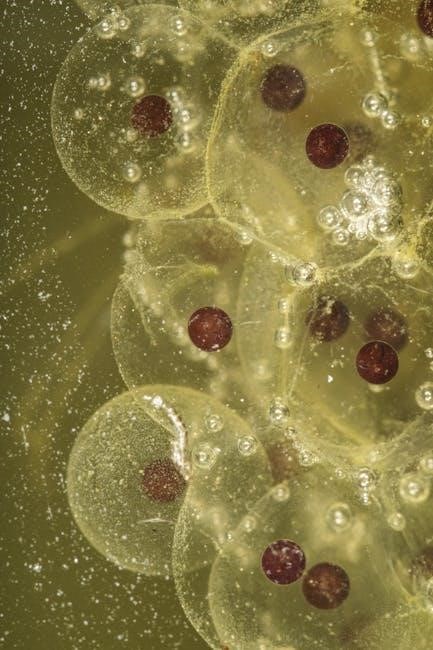
Initially‚ the single-celled zygote undergoes rapid cleavage‚ forming a blastodisc on day one. Subsequent stages‚ including the formation of the area opaca and pellucida‚ precede the crucial appearance of the primitive streak around day three – a key organizer of embryonic axes.
Gastrulation (stages 4-7) establishes the three germ layers – ectoderm‚ mesoderm‚ and endoderm – essential for organogenesis. The heart becomes visible relatively early‚ around 24 hours of incubation‚ and by day seven‚ distinct structures like wing and foot digits emerge.
Later stages involve continued organ refinement‚ yolk sac absorption‚ and positioning for hatching‚ all meticulously charted in embryological resources. These PDF resources are invaluable for students and researchers alike‚ offering a detailed understanding of vertebrate development.
Importance of Studying Chick Embryo Development

Studying chick embryo development is paramount due to its accessibility and external development‚ allowing for direct observation of embryogenesis without invasive procedures. Detailed chick embryo development stages PDF guides serve as essential resources for researchers and educators.
The chick embryo acts as a powerful model for understanding vertebrate development‚ offering insights into fundamental biological processes like cell differentiation‚ organogenesis‚ and angiogenesis. Observing the chronological scheme of development‚ from initial segmentation to the formation of embryonic annexes‚ provides crucial data.
Furthermore‚ the chick embryo facilitates studies on angiogenesis and vasculogenesis‚ as demonstrated in ex-ovo development models. The availability of comprehensive visual guides‚ including posters and diagrams‚ enhances understanding of each stage;
Its relatively large size and rapid development make it ideal for experimental manipulation‚ contributing significantly to our knowledge of embryonic origins and potential developmental abnormalities. Access to detailed PDF documentation is therefore critical for advancing embryological research.
The First Three Days: Initial Stages
Chick embryo development begins with blastodisc formation‚ progressing through area opaca/pellucida‚ and culminating in the appearance of the primitive streak – detailed in PDF guides.
Day 1: Blastodisc Formation
Day 1 of chick embryo development marks the initial stages following fertilization‚ vividly illustrated in comprehensive chick embryo development stages PDF resources. The blastodisc‚ a small‚ circular‚ whitish spot on the yolk surface‚ represents the earliest visible sign of embryonic activity. This disc comprises a cluster of cells‚ the blastomeres‚ resulting from the initial cleavages of the fertilized egg.
Initially‚ the blastodisc appears relatively uniform‚ but subtle changes begin to occur as cells divide and migrate. These early divisions are holoblastic‚ meaning the egg undergoes complete cleavage‚ though this is obscured by the large yolk mass. Detailed PDF guides often showcase microscopic images of the blastodisc at this stage‚ highlighting the cellular arrangement. The formation of the blastodisc is crucial as it establishes the foundation for all subsequent developmental events‚ setting the stage for gastrulation and organogenesis. Understanding this initial phase is fundamental when studying embryogenesis‚ and readily available in visual charts.
Day 2: Area Opaca and Area Pellucida
Day 2 in chick embryo development witnesses the differentiation of the blastodisc into two distinct regions: the area opaca and the area pellucida‚ clearly depicted in chick embryo development stages PDF guides. The area opaca‚ a dense‚ opaque zone‚ surrounds the central area pellucida‚ which is translucent. This distinction arises from differences in cell density and yolk distribution.
The area pellucida is the site where the primitive streak will eventually form‚ initiating gastrulation. It contains the cells destined to become the embryo proper. The area opaca provides nourishment to the developing embryo and contributes to extraembryonic membranes. Visual aids‚ such as those found in detailed PDFs‚ emphasize the contrasting appearances of these two areas. Studying these early divisions is crucial for understanding the subsequent formation of germ layers and organ systems‚ as illustrated in embryology charts.
Day 3: Primitive Streak Appearance

Day 3 marks a pivotal moment in chick embryo development: the appearance of the primitive streak. This structure‚ prominently featured in chick embryo development stages PDF resources‚ is a thickened line on the epiblast within the area pellucida. It signifies the beginning of gastrulation‚ a process fundamental to establishing the three germ layers – ectoderm‚ mesoderm‚ and endoderm.
Cells from the epiblast migrate through the primitive streak‚ initiating the formation of these layers. The streak extends from the posterior end of the embryo and acts as an organizer‚ directing cell movements and defining the body plan. Detailed PDF guides and embryological charts visually demonstrate this crucial step. Understanding the primitive streak’s formation is essential for comprehending how the single-layered blastula transforms into a trilaminar embryo‚ setting the stage for organogenesis.

Stages 4-7: Gastrulation and Early Organogenesis
Stages 4-7‚ detailed in chick embryo development stages PDF guides‚ showcase gastrulation and initial organ formation‚ establishing fundamental body structures.
Stage 4: Formation of the Epiblast
Stage 4 of chick embryo development‚ comprehensively illustrated in chick embryo development stages PDF resources‚ marks a pivotal moment: the formation of the epiblast. This crucial step initiates gastrulation‚ a process where cells migrate and reorganize to establish the three primary germ layers – ectoderm‚ mesoderm‚ and endoderm – which will ultimately give rise to all tissues and organs.
The epiblast‚ originating from the blast disc‚ becomes the source of these germ layers. Detailed diagrams within these PDF guides visually demonstrate how cells begin to differentiate and arrange themselves. This stage is characterized by a distinct thickening of the blast disc‚ signaling the commencement of complex developmental processes. Understanding the epiblast’s formation is fundamental to grasping the subsequent stages of organogenesis‚ as it lays the groundwork for the embryo’s body plan. The formation of the epiblast is a cornerstone in understanding embryogenesis.
Stage 5: Neural Plate Development
Stage 5 in chick embryo development‚ meticulously documented in chick embryo development stages PDF guides‚ witnesses the emergence of the neural plate – a precursor to the central nervous system. This flat sheet of cells forms from the epiblast and is crucial for the development of the brain‚ spinal cord‚ and peripheral nerves.
PDF resources showcase the neural plate as a distinct‚ elongated structure along the midline of the embryo. Its formation initiates neurulation‚ a process vital for establishing the body’s control center. The neural plate’s development is a key indicator of healthy embryogenesis. As cells within the plate proliferate and differentiate‚ they prepare to fold and form the neural folds‚ ultimately creating the neural tube. Understanding this stage is essential for comprehending neurological development and potential congenital defects‚ as detailed in embryological studies.
Stage 6: Neural Folds and Somites
Stage 6 of chick embryo development‚ comprehensively illustrated in chick embryo development stages PDF materials‚ marks significant progress in both neural and musculoskeletal systems. The neural plate begins to elevate‚ forming neural folds along its edges. These folds will eventually fuse to create the neural tube‚ enclosing the developing spinal cord.
Simultaneously‚ PDF guides depict the appearance of somites – paired blocks of mesoderm that flank the neural tube. These somites are precursors to vertebrae‚ ribs‚ and skeletal muscles. Their segmentation is a hallmark of this stage‚ providing the foundational pattern for the axial skeleton. The coordinated development of neural folds and somites is critical for proper body plan formation. Observing these structures in PDF diagrams aids in understanding the complex interplay between the nervous and musculoskeletal systems during embryogenesis.
Stage 7: Wing and Foot Digit Formation‚ Heart Enclosure
Stage 7 in chick embryo development‚ clearly visualized in detailed chick embryo development stages PDF resources‚ showcases dramatic advancements in limb and cardiovascular development. Budding limbs begin to exhibit distinct digit formation‚ with early outlines of future wing and foot structures becoming apparent. These PDF guides illustrate the progressive separation of digits‚ a crucial step in limb morphogenesis.
Concurrently‚ the heart achieves complete enclosure within the thoracic cavity‚ a vital milestone for circulatory system function. This enclosure‚ documented in PDF diagrams‚ protects the developing heart and facilitates efficient blood pumping. By this stage‚ the embryo increasingly resembles a bird‚ as noted in developmental descriptions. Studying these features through PDF materials provides a comprehensive understanding of organogenesis and morphological changes during this critical phase.
Days 8-10: Continued Organogenesis
PDF resources detail how organ systems differentiate rapidly during days 8-10‚ with limb development progressing and feathers/beaks beginning to form.
Day 8: Differentiation of Organ Systems
On day 8 of chick embryo development‚ a significant period of organogenesis unfolds‚ meticulously documented in various chick embryo development stages PDF guides. These resources illustrate the increasing complexity as distinct organ systems begin to differentiate and specialize.
The heart‚ already enclosed within the thoracic cavity by day 7‚ continues its refinement‚ becoming more structurally defined. Blood vessels become increasingly prominent‚ facilitating nutrient and oxygen transport to the rapidly developing tissues. The neural tube is further established‚ laying the groundwork for the central nervous system.
Limb buds elongate‚ and initial signs of digit formation become apparent‚ though still rudimentary. The digestive system undergoes further regionalization‚ with the formation of the esophagus and intestines. Muscle development commences‚ contributing to the embryo’s increasing motility. Detailed PDF charts showcase these advancements‚ providing a visual timeline of this crucial stage. Observing these changes is fundamental to understanding vertebrate embryology.
The embryo itself occupies a larger portion of the egg’s interior‚ demonstrating the rapid pace of growth and development.
Day 9: Further Development of Limbs
Day 9 marks a period of substantial progress in limb development‚ comprehensively illustrated within chick embryo development stages PDF resources. These visual guides demonstrate the continued elongation of both wing and leg buds‚ with a noticeable refinement in their shape and structure.
The digits‚ previously appearing as small swellings‚ begin to become more defined‚ although they remain webbed. Cartilage formation accelerates within the limb buds‚ providing skeletal support for the developing appendages. Muscle precursors proliferate‚ preparing for coordinated movement.
The circulatory system continues to expand‚ ensuring adequate blood supply to the growing limbs. The nervous system extends into the limb buds‚ establishing innervation for future muscle control. Detailed PDF diagrams highlight these intricate changes‚ showcasing the precise timing of developmental events.
The embryo’s overall size increases‚ reflecting the energetic demands of rapid growth. Observing these advancements is crucial for understanding vertebrate limb formation and embryological processes.
Day 10: Feather and Beak Development
Day 10 witnesses the emergence of key avian characteristics: feather and beak development‚ meticulously documented in chick embryo development stages PDF guides. Feather tracts become visibly apparent as small buds along the skin‚ precursors to the future plumage. These tracts indicate where feathers will eventually emerge‚ providing insulation and aiding in flight.
Simultaneously‚ the beak begins to harden and take shape‚ transitioning from a soft‚ cartilaginous structure to a more defined form. This process is crucial for the embryo’s ability to peck through the shell during hatching. The head region undergoes significant remodeling‚ with the beak becoming increasingly prominent.
PDF resources illustrate the precise location and progression of these developments. Internal organ systems continue to mature‚ supporting the growing embryo’s needs. The circulatory system further expands‚ delivering nutrients and oxygen to developing tissues. Observing these changes provides insight into avian-specific embryological processes.

Days 11-14: Advanced Development
Chick embryo development stages PDFs detail organ system refinement during this period‚ alongside reproductive system development‚ crucial for future viability.
Growth accelerates‚ preparing the embryo for the final stages of incubation and eventual hatching.
Stage 14: Organ System Refinement
Stage 14 in chick embryo development‚ comprehensively documented in chick embryo development stages PDF resources‚ marks a period of intense organ system maturation and functional preparation.
The circulatory system achieves full functionality‚ with the heart efficiently pumping blood to support the rapidly growing tissues. Digestive organs become increasingly differentiated‚ preparing for post-hatch nutrient processing. Respiratory structures continue to develop‚ enhancing gas exchange capabilities.
Skeletal ossification progresses‚ providing structural support and enabling movement. Neurological development is also significant‚ with increasing complexity in brain structures and neural pathways. Detailed PDF guides illustrate these changes‚ showing the precise timing of organ maturation.
This stage represents a critical checkpoint‚ ensuring that all essential systems are adequately refined before the embryo enters the final phases of preparation for hatching. Visual aids within the PDFs are invaluable for understanding these intricate processes.
Development of the Reproductive System
The development of the reproductive system in the chick embryo‚ meticulously charted in chick embryo development stages PDF guides‚ begins to differentiate during later stages‚ though full functional maturity occurs post-hatching.
Gonadal ridges appear‚ eventually developing into the testes in males or the ovary in females. Primordial germ cells migrate to these ridges‚ initiating gametogenesis. The Müllerian ducts‚ precursors to the oviduct in females‚ and the Wolffian ducts‚ which contribute to male reproductive structures‚ begin to form.
PDF resources detailing chick embryo development showcase the progressive differentiation of these structures‚ highlighting the hormonal influences driving their formation. While the system isn’t fully functional in ovo‚ the foundational architecture is established.
Understanding this process provides insights into vertebrate reproductive biology and the genetic mechanisms governing sex determination. These PDFs offer a valuable visual reference for embryologists and students alike.

Days 15-18: Preparation for Hatching
Chick embryo development stages PDFs reveal yolk sac absorption intensifies‚ providing nourishment. The embryo positions itself for hatching‚ preparing for its emergence from the egg.
Yolk Sac Absorption
Chick embryo development stages PDF resources clearly demonstrate the critical role of yolk sac absorption during the final stages of incubation. As the embryo nears hatching‚ its reliance on the yolk sac as a primary nutrient source dramatically increases. This process isn’t simply a matter of consumption; it’s a carefully orchestrated physiological event.

The yolk sac‚ initially a large‚ visible structure‚ progressively shrinks as its contents – proteins‚ fats‚ and vital vitamins – are drawn into the developing embryo’s circulatory system. Detailed diagrams within these PDF guides illustrate how the yolk sac is physically drawn into the embryo’s body cavity‚ maximizing nutrient uptake. This absorption is essential for providing the energy required for the final stages of organ refinement and the physical exertion of hatching.
Furthermore‚ the absorption process contributes to the embryo’s overall size and weight gain‚ preparing it for life outside the protective shell. Observing this stage through developmental charts highlights the efficiency of this nutrient transfer‚ showcasing a remarkable example of biological adaptation.
Positioning for Hatching
Chick embryo development stages PDF guides meticulously document the crucial repositioning phase preceding hatching. Around day 18‚ the embryo shifts from a lateral position within the egg to a more upright posture‚ with its head tucked under its right wing. This precise positioning isn’t random; it’s essential for successful pipping and eventual emergence.
Detailed illustrations in these PDF resources reveal how the embryo rotates‚ aligning its beak with the air cell for the first breath. This maneuver requires significant muscular effort and coordinated movements‚ demonstrating the embryo’s advanced neurological development. The positioning also ensures the beak is optimally placed to initiate the cracking of the shell.
Observing this stage through developmental charts emphasizes the importance of proper egg handling during the final days of incubation‚ as disturbances can disrupt this critical positioning process. Successful hatching hinges on this final‚ carefully orchestrated preparation.
Days 19-21: Hatching
Chick embryo development stages PDFs detail the final phase: internal and external pipping‚ culminating in hatching completion.
These resources visually demonstrate the chick’s emergence‚ a pivotal moment in its life cycle.
Internal Pipping
Internal pipping‚ meticulously documented in chick embryo development stages PDF guides‚ marks the initial stage of hatching‚ typically occurring around day 19-20 of incubation. This crucial process involves the chick’s beak breaking through the air sac within the egg‚ providing its first breath of air.
Detailed diagrams within these PDF resources illustrate how the chick positions itself for this maneuver‚ utilizing its egg tooth – a small‚ temporary projection on its beak – to penetrate the shell’s inner membrane. This action isn’t visible externally‚ hence the term “internal.” The chick then begins to breathe air from within the egg‚ gradually depleting the air sac’s oxygen.
These guides emphasize that internal pipping is a vital preparatory step‚ allowing the embryo to transition from relying on the yolk sac for respiration to utilizing its lungs; Observing this stage requires careful candling‚ and PDFs often include images demonstrating the subtle changes indicating successful internal pipping. It’s a delicate process‚ and maintaining proper humidity is crucial for successful hatching.
External Pipping and Hatching Completion
External pipping‚ clearly illustrated in chick embryo development stages PDF resources‚ follows internal pipping and signifies the visible breakthrough of the beak through the eggshell. This typically occurs within 24-48 hours of internal pipping‚ around days 20-21 of incubation. Detailed PDF diagrams showcase the chick’s methodical pecking‚ creating a star-shaped crack in the shell.
These guides emphasize the importance of not assisting the chick during this phase‚ as intervention can disrupt the natural process and potentially harm the developing bird. The chick continues to chip away at the shell‚ gradually enlarging the opening.
Finally‚ hatching completion involves the chick fully emerging from the egg‚ a process that can take several hours. PDFs often include timelines and images depicting the chick’s exhausted but triumphant state. Post-hatch‚ the chick requires warmth and access to food and water‚ as detailed in comprehensive chick embryo development guides.